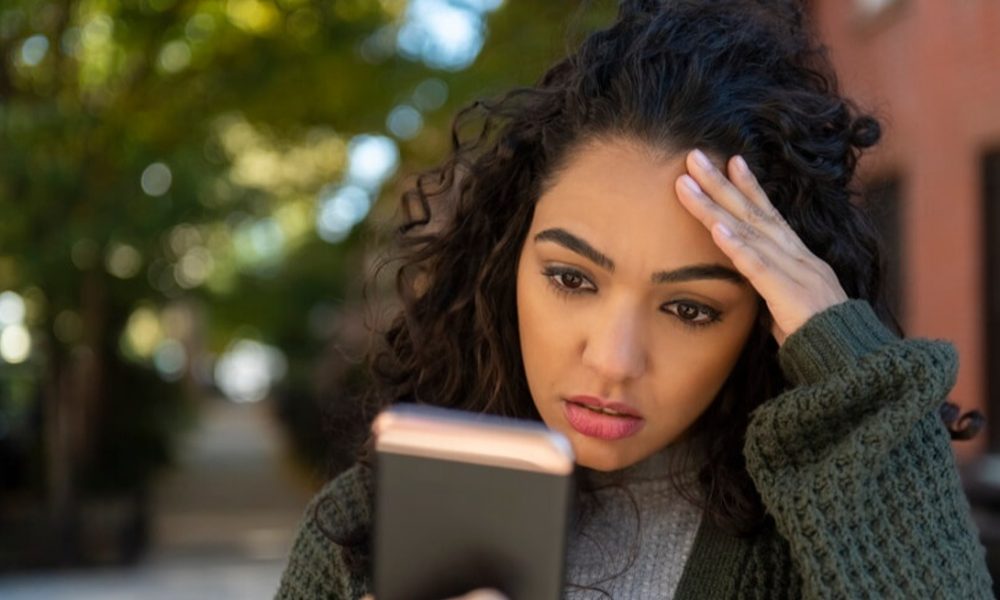


Do you feel like you have an invisible barrier stopping you from achieving your goals?
Chronic stress can often feel like that. It’s not always easy to spot people suffering from chronic stress, but its effects are pervasive.
Let’s explore what chronic stress means, how it can affect you, and how you can treat it.
What is chronic stress?
A study published in the Journal of International Medical Research offers this chronic stress definition.
Generally, the term chronic stress refers to a systemic reaction that happens in the body caused by both negative internal and negative external factors. Chronic stress typically occurs over an extended period of time.
In short, chronic stress happens when you experience stress over a long period. This stress can come from a variety of sources.
Over time, symptoms can start appearing and begin affecting your daily life. It’s different from regular good or bad stress because of how pervasive it is. Let’s take a look at symptoms of chronic stress and how to cope.
4 chronic stress symptoms
What does it feel like to suffer from chronic stress? Here are four typical symptoms of chronic stress:
1. Fatigue
The toll that chronic stress puts on someone’s body can lead to chronic fatigue and emotional exhaustion. It can also lead to difficulty sleeping which further aggravates fatigue.
As a result, someone with chronic stress will often feel irritable. They can also have low energy levels.
2. Pain
Chronic stress doesn’t just make you feel tired. It can also cause pain, discomfort throughout the body, and/or physical exhaustion.
Someone with chronic stress may experience:
- Headaches
- Muscle tension
- Gastrointestinal issues
- General aches and pains
3. Feeling helpless
Chronic stress goes beyond physical sensations. It can also put a heavy strain on someone’s mental health.
Someone dealing with chronic stress may often feel helpless to improve their situation. They can feel a loss of control over their life. It can even go as far as to cause an existential crisis.
4. Issues with concentration
Finally, chronic stress can cause disruptions in concentration and make it difficult to focus. This can lead to disorganized thinking. People struggling with chronic stress may also experience nervousness and anxiety.

What causes chronic stress?
It can be difficult to pinpoint exactly what causes chronic stress in someone’s life. The stress will usually stem from several issues.
Here are four examples of what can cause or aggravate chronic stress.
1. A dissatisfying or demanding job
When someone doesn’t love the work they do, it can contribute to chronic stress. This is especially true if your work is dissatisfying or demanding.
Other job factors that can contribute to chronic stress include:
- Feeling unhappy in your work environment
- Working under poor management
- Dealing with unclear expectations
- Having no say in the decision process
- Feeling insecure about your chances for a promotion
Working long hours can also worsen the symptoms of chronic stress.

2. Stress at home
Even if things are going well at work, chronic stress can stem from your home life, too. Work-life balance can get challenging if you’re feeling lots of pressure at home.
There can be a lot on your plate if you’re caring for elderly family members and children.
Other examples of stress factors at home can include:
- Divorce
- Bereavement
- Moving to a new home
- Health problems
- Relationship challenges
The stress from your home can be worse if your job doesn’t support working parents adequately.
3. Discrimination or harassment
Someone who isn’t a part of the dominant culture can experience chronic stress from discrimination, harassment, or coercion.
An example of this is if your ideas are thrown out based on your gender, race, sexual orientation, or religious beliefs.
Even if you don’t experience explicit discrimination or harassment, you can still experience chronic stress from:
- Microaggressions
- Feeling like you don’t belong
- Not feeling heard
This is another reason diversity is crucial in the workplace.
4. Financial problems
If you’re experiencing financial problems, these can weigh on you over time and contribute to chronic stress.
Examples of financial stress can include:
- Living paycheck to paycheck
- Paying off debt
- Struggling to set aside enough money for retirement
- Paying for kids’ college tuition
Plus, financial problems can also contribute to other issues, such as putting stress on a relationship.
4 types of chronic stress
There’s more than one type of chronic stress that can show up. Here are the four main types of chronic stress that may affect you.
1. Work stress
Work stress comes from experiences or environments that come from the workplace. Any leadership challenges or pressure stemming from your job or your workplace fall into this category.
For example, a lack of proper project management could cause you to always work overtime to deliver milestones on time.
If this problem is pervasive, the long-term work stress caused by this issue could turn into chronic stress. And it could manifest itself in other areas of your life.
2. Environmental stress
Your surroundings may cause environmental stress. This could be the environment you live in, work in, or spend lots of time in for other reasons.
Some environmental stressors aren’t as obvious as other sources of stress in your life. For example, living in a loud and busy neighborhood in the city could cause stress over time. Also, struggling with your work-life balance can also cause stress.
But it wouldn’t necessarily be easy to notice the impact this type of environment has on you unless you were to spend time elsewhere. Stressors like pollution, electromagnetic radiation, or temperature are other examples of environmental components that can easily go unnoticed.
Other environmental stressors are more obvious. For instance, harsh lighting at work could be impacting your mood.
Natural disasters like hurricanes or snowstorms are also obvious stressors that can contribute to someone’s stress levels.

3. Relationship stress
Personal relationships can become another source of chronic stress. This is especially true when you have to deal with people who don’t respect your boundaries, such as toxic leaders or abusive partners.
But relationship stress can show up in less obvious ways, even when someone isn’t outright toxic or abusive. For example, you can feel stressed from the high expectations of someone you care about places on you.
You may also have a strained relationship with a child or parent. Even friendships can become a source of relationship stress when you don’t assert your boundaries.
For example, you may always say yes to helping out friends, even when it goes against your self-care needs.
4. Emotional stress
Emotional stress can come from the everyday struggles and pressures you face in your life. Feeling sad, worried, angry, or fearful are all normal emotional reactions.
But sustained emotional stress can develop into chronic stress. Some examples of long-term emotional stress could include:
- Prolonged grief after losing a loved one
- Worrying about finances or health problems
- Anger over social issues and injustices
- Fear over a long-term threat (like a pandemic)
Work, environmental, and relationship stress can contribute to emotional stress as well.
Chronic stress effects
One of the reasons chronic stress is so serious is its implications on your overall wellness.
The effects chronic stress can have on your well-being don’t just affect your work performance. It can have a huge impact on your physical health and mental health.
Here are just five of the effects of chronic stress that can affect people over time.
1. Increased chance of cardiovascular disease
Studies have shown that chronic stress is a contributing factor of cardiovascular disease. One of the reasons is because it can cause high blood pressure.
Examples of cardiovascular disease include:
- Heart failure and heart attacks
- Heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy)
- Coronary artery disease
- Aorta disease and Marfan syndrome
- Arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythms)
Currently, heart disease is the leading cause of death in the US.

2. Increased risk of developing cancer
According to the Frontiers in Oncology journal, chronic stress can promote cancer development.
They state that because of this, cancer patients and healthy people can both benefit from stress management.
According to the CDC, cancer is the second most common cause of death in the US.
3. Changes in the brain
According to research published in the Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology journal, chronic stress can reduce the size of the hippocampus. The hippocampus is a part of the brain that has a significant impact on learning and memory.
As a result, chronic stress can cause “impairments in attention, memory, and emotional processing.”
4. Effects on the entire body
Chronic stress can also wreak havoc on the digestive system. For instance, it can cause colitis or worsen inflammatory bowel disease. This is because chronic stress disturbs the microbiome in the gut.
In addition to the above effects, chronic stress can also have an impact on the entire body, including your nervous system, muscles, immune system, and hormones.
5. Insomnia
Difficulty falling asleep and staying asleep is a typical symptom of chronic stress.
Coupled with racing thoughts, the physical symptoms of chronic stress (like shallow breathing and a raised heart rate) can make it challenging to fall asleep. Over time, if chronic stress isn’t treated, it can lead to insomnia.
How is chronic stress treated?
Chronic stress can be treated regardless of its severity.
For less severe conditions, you can use stress management techniques to reduce or prevent chronic stress, such as:
- Physical activity
- A healthy diet
- Good sleeping habits
- Relaxation techniques to help you calm down like mindful breathing, meditation, or yoga.
But more severe cases of chronic stress require support from health professionals who can show you how to relieve stress or take further measures.
Your medical practitioner may recommend psychotherapy with a licensed therapist. A therapist can use several different psychotherapy techniques to treat chronic stress, including:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Psychoanalysis therapy
- Humanistic therapy
- Integrative therapy
- EMDR
Additionally, your doctor may prescribe medications to help treat or manage your symptoms of chronic stress.
Keep in mind that you don’t need to wait until your chronic stress reaches a certain level of severity to consult a healthcare professional.
If you feel like chronic stress has a negative impact on your life, even if it seems small, don’t hesitate to ask for help.
4 benefits of stress management techniques to cope with chronic stress
Stress management techniques can reduce the impact of chronic stress, and you may also experience other benefits. Here are four examples of what stress management techniques can do for you.
1. Increased physical health
Using stress management techniques like mindful breathing and physical exercise can positively impact your health.
These techniques by themselves can improve physical health. And, because they also help fight chronic stress, you’ll get a double benefit.

2. Better productivity
Fighting chronic stress can make you more productive at work.
Since chronic stress can cause impairments in attention, memory, and emotional processing, too much chronic stress can negatively impact your productivity.
On the other hand, keeping your chronic stress levels in check can allow you to regain your productivity.
3. Improved sleep
Chronic stress can have a negative impact on the quality of your sleep. One of the reasons is because it can influence your circadian rhythm. When you implement stress management techniques and treatments, you can improve your sleep.
Some techniques may even improve your sleep on their own, even if they don’t impact your stress levels immediately. For instance, mindful breathing can help you quiet your mind and slow your heart rate so you can fall asleep faster.
Physical exercise can help adults with insomnia improve their sleep and their quality of life.
4. More fulfilling personal relationships
Finally, managing your chronic stress can help you build more fulfilling relationships. This is true at work and in your home life.
When chronic stress has less of a hold on your health and your mood, you can be your best self with other people in your life. You have greater emotional bandwidth to provide support to those you love when your own cup is filled.
Make your well-being a priority with chronic stress management
If chronic stress is part of your reality, it’s important to prioritize stress management to care for your mental health.
Mental health doesn’t just have an impact on your physical well-being. It can also determine your quality of life.








You must be logged in to post a comment Login